Duality: conversion summary#
This is a summary of the recommended approach to convert a primal problem into its dual problem.
First, you convert the primal problem to a standard form:
Minimisation.
All constraints of the form
All variables with bound
Second, you convert the standard-form primal problem into the dual problem, as illustrated in Fig. 1 and written out in the bullet point list below:
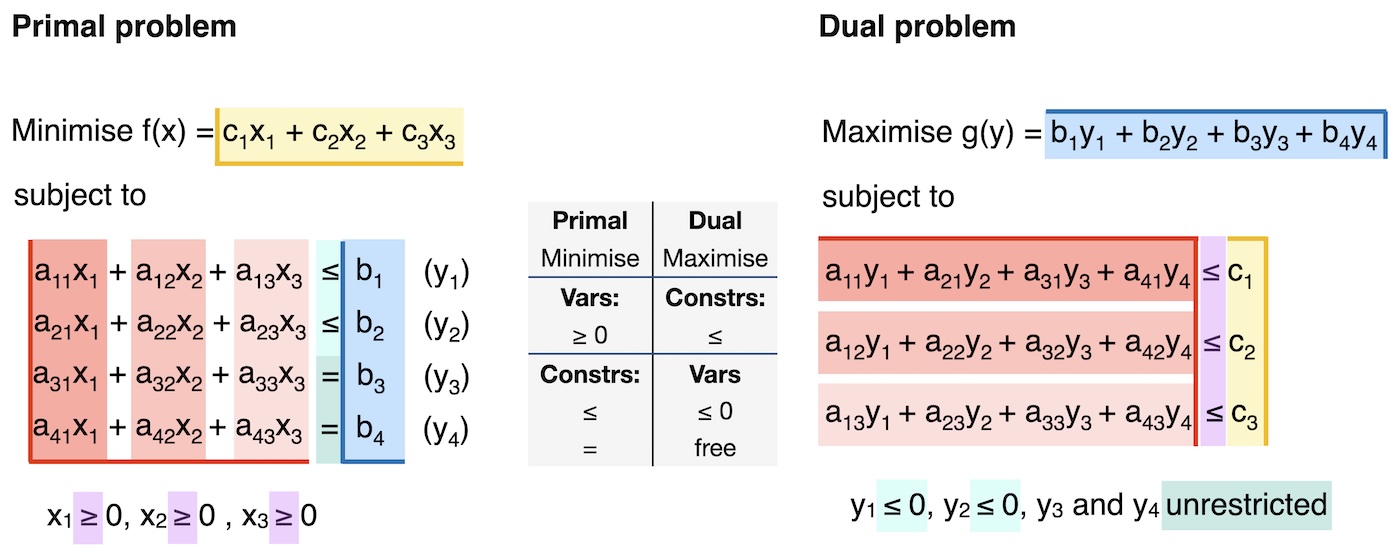
Fig. 1 Illustration of the conversion from standard form primal problem to dual problem.#
The primal objective function coefficients,
The primal constraint parameters,
The primal constraints in
The primal constraints in
The primal variables
The constraint coefficient